Sustainable refrigeration in industrial kitchens and supermarkets with R290
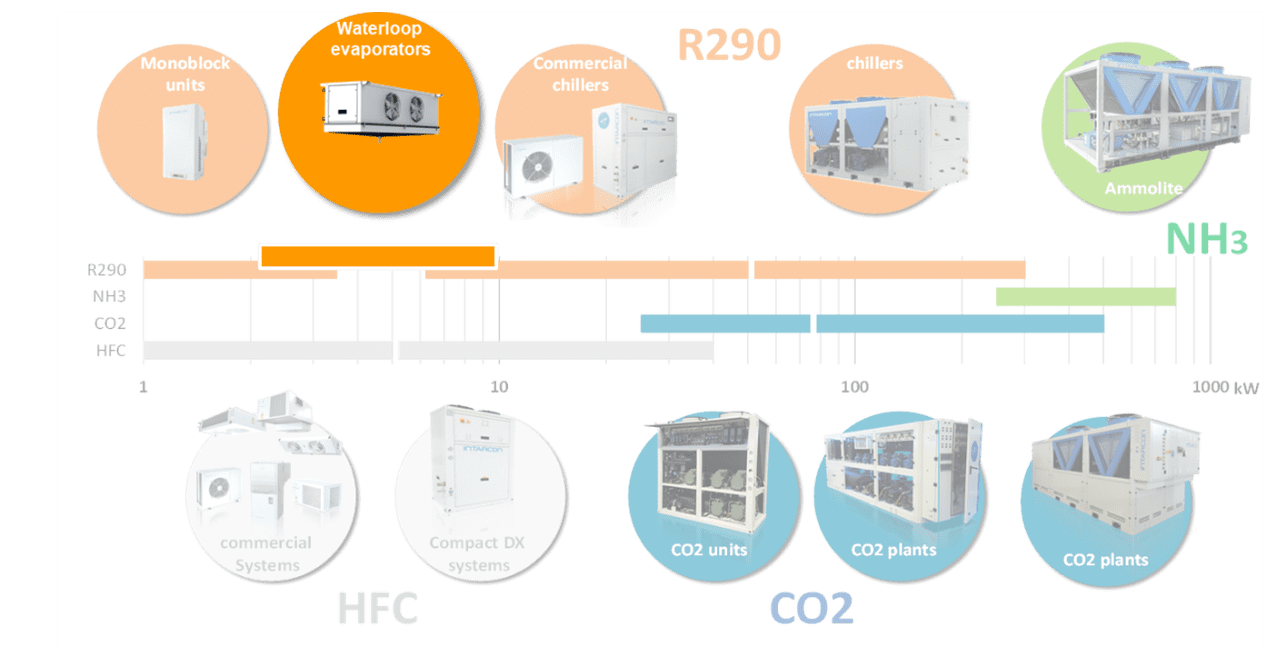
INTARCON2022-06-03T10:02:08+02:00If we look at the commercial refrigeration sector in the cooling capacity range, we can see that propane (R290) has been confirmed as the best natural refrigerant in small commercial equipment such as refrigerated cabinets, display cabinets and compact commercial units for small cold rooms in industrial kitchens and supermarkets.
R290 is also being successfully used in medium and large capacity glycol chiller plants, exceeding other natural refrigerants, where these solutions have replaced and continue to progressively replace HFCs.
Product range – INTARCON
However, there is a range in the cooling capacity range where R290 or other natural refrigerants can’t easily replace HFCs, it is difficult for natural refrigerants to compete with them. This range refers to small commercial applications with semi-compact equipment in the range of 2 to about 8 or 10 kW.
This range is too small for CO2 to be competitive and too large for compact units with R290. We find many applications in this range, such as cold rooms of a size between 10 to 50 m3, often used in commercial refrigeration in food shops, supermarkets, restaurants and small industries.
Sustainable refrigeration in industrial kitchens and supermarkets with R290.
To provide a solution to this need, INTARCON has developed a new range of equipment called Waterloop Evaporators, which can replace the traditional condensing unit connected to one or two direct expansion evaporators with HFC (R449A or R134a) using R290 in the refrigeration circuit, thus completing the commercial refrigeration range.
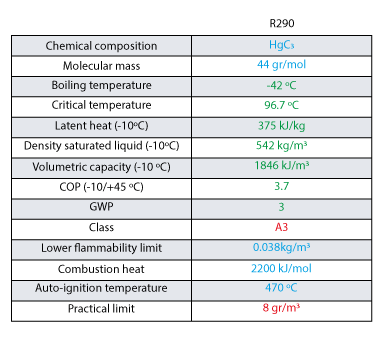
Properties of propane refrigerant gas, R290.
Propane has excellent performance and thermal properties:
- R290 has a suitable boiling point, similar to that of R404A.
- The theoretical efficiency in a single-stage cycle is quite high, thus corroborating its efficiency.
- Low liquid density and high latent heat which means a lower refrigerant charge is required to obtain the same cooling capacity.
- Low molecular mass with small polytropic coefficient leading to moderate discharge temperature, low viscosity and lower pressure drop.
However, the main disadvantage of R290 is its flammability (class A3). Its practical limit is very low (8 g/m3 chamber volume). This implies that the maximum allowable load in a system is low, especially when R290 is used indoors in publicly accessible premises. Here we are limited to compact and small power systems as the only acceptable solution.
Technical features:
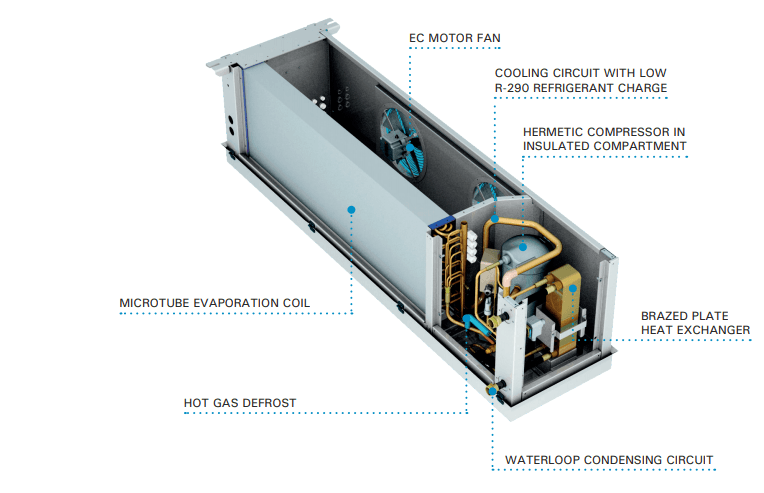
The waterloop evaporator units with built-in compressor. It is a hermetically sealed compact system for installation inside small cold rooms. They are pre-charged with a small charge of natural refrigerant R290, less than the practical limit of refrigerated volume and less than 500 g, so they are exempt from the RSIF Regulation and EN 378.
Features:
- 230 V-I-50 Hz power supply. Available in 60 Hz. Other voltages by request.
- R290 refrigerant charge low than 0.15 kg.
- Bodywork in aluminium sheet and structure in galvanised steel lacquered in polyester paint.
- Hemetic compressor integrated in thermally insulated compartment, with crankase heater.
- Refrigeration circuit in annealed copper tube, with high pressure switch, filter drier and load valve.
- Evaporation coil in copper pipes and aluminium fins, thermostatic expansion valve and hot gas defrost.
- EC motor fans.
- Brazed plates heat exchanger.
- Threaded hydraulic connections.
- Control panel in white lacquered sheet metal cabinet, with MCB protection and multifunction electronic regulation.
- 3 m interconnection cable.
In the following image we can see all the components mentioned above:
Advantages and disadvantages.
Plug & Play system:
- Propane is a natural refrigerant, at a low cost, with no greenhouse effect, and with high energy efficiency. In addition, the equipment is pre-charged with R290, tested and adjusted in the factory.
- It only requires connection to the water loop for condensation. In most installations water can be used as a secondary fluid without the need for glycol and the circuit is normally developed in PVC or PPR pipe without the need for insulation allowing easy modification and expansion.
Development and security:
- Decentralised refrigeration production provides a high level of operational reliability for the system, guaranteeing high system availability in the event of a single unit failure.
- Freeze protection is included, which protects the equipment against low ambient temperature.
- Tropicalised system up to 45ºC ambient temperature, with condensing water temperatures up to 55ºC, and without the need for additional cooling equipment.
55 ºC, and without the need for additional cooling equipment. - Reduced R290 load without safety risks.
In addition, it has the following benefits over traditional direct expansion systems:
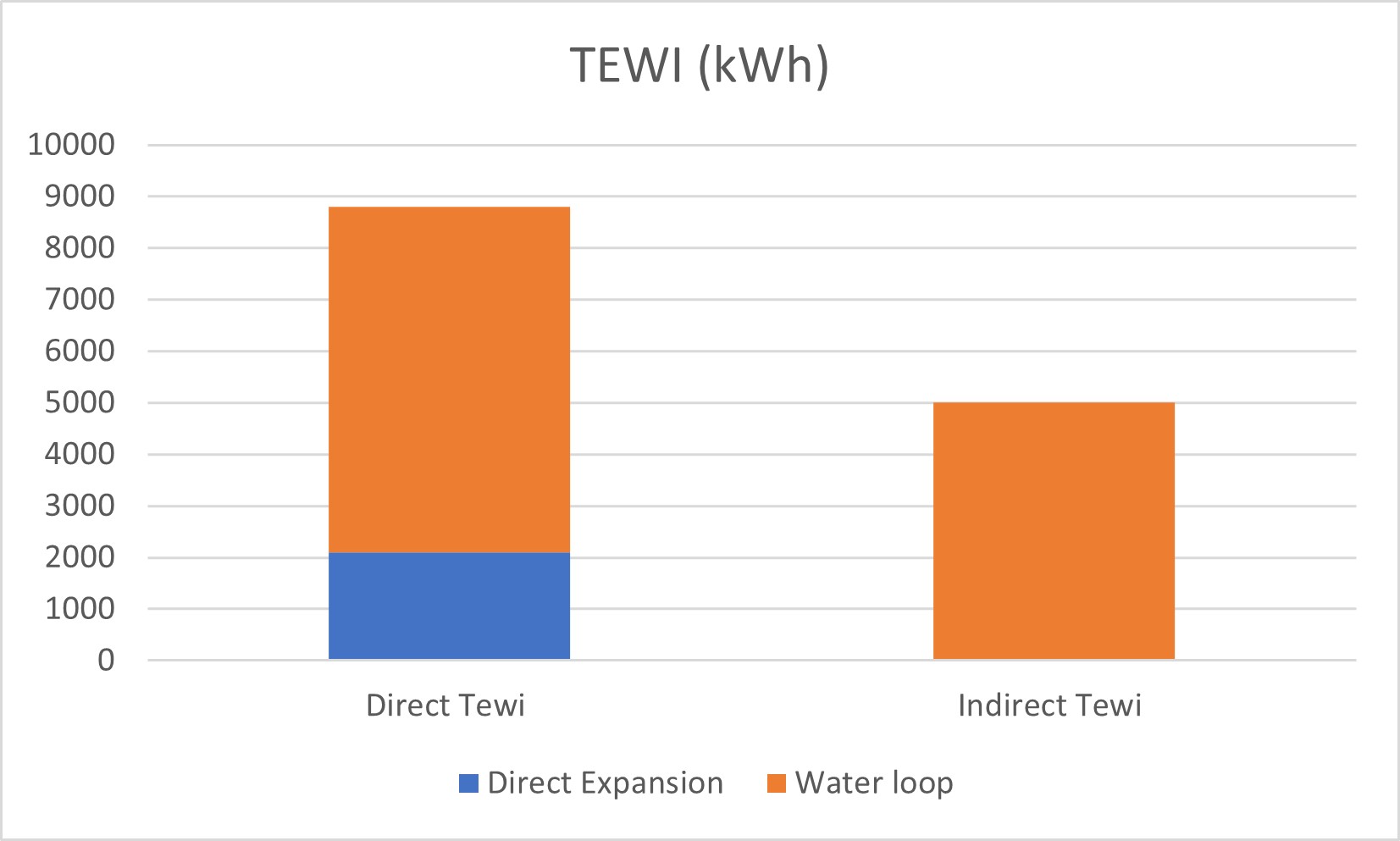
Significant reduction of TEWI (Total Equivalent Warming Impact)
The waterloop system with R290 thas a considerably lower GWP (GWP=3) compared to HFCs so that the direct TEWI is practically null. As for the indirect TEWI, the compressor consumption is slightly favoured thanks to the efficiency of R290. This makes it a long-term solution probably exempted from F-Gas regulation in the future.
Reduction of the annual consumption of the installation
The energy consumption is expected to be lower than a conventional direct expansion system. Even if the COP in indirect systems is normally lower than in direct systems, this is partially compensated by the higher efficiency of R290. Still, the nominal COP might be a bit lower in water loop systems above 32 °C ambient temperature, although if we consider seasonal efficiency, in an indirect condensing water loop system the compressor would condense lower as a direct expansion system would normally force a higher condensing pressure by regulating the rotational speed of the condenser fans.
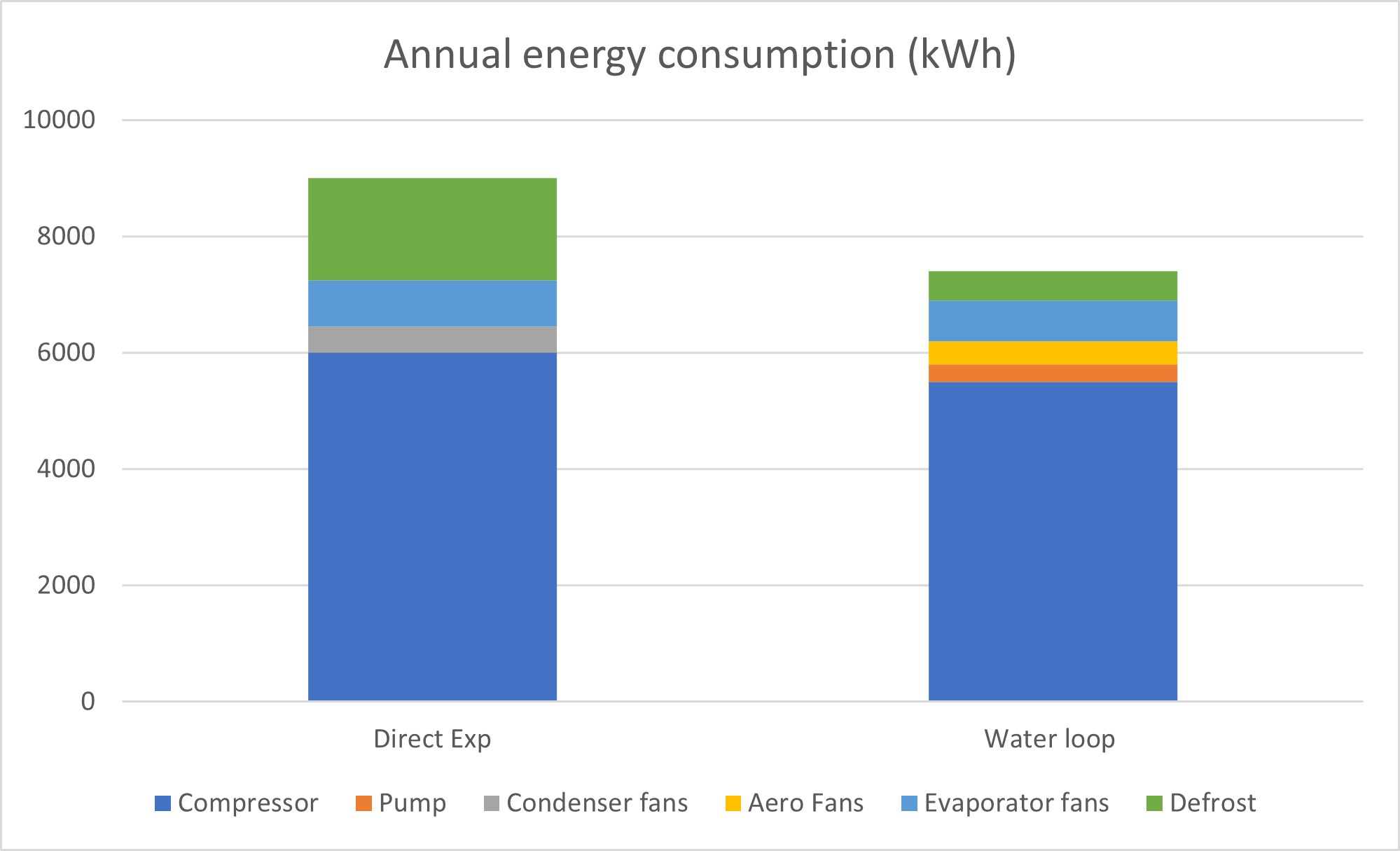
The following graph shows a comparison between a semi-compact direct expansion system and a waterloop evaporator where we have considered each additional energy consumption (air cooler and circulation pump). Although an indirect condensing system is around 25% more expensive than a semi-compact solution, it shows that the initial cost overrun can be recovered in a moderate payback period.
Thanks to these advantages and benefits, waterloop evaporators are expected to replace traditional refrigeration systems as the definitive, efficient and safe solution.