Energy Efficiency in Industrial Refrigeration – Part 3: Digitalisation and Control Optimisation
Control systems in industrial refrigeration are fundamental for optimising operations and improving energy efficiency across facilities.
In this third part of our series, we examine their impact on overall system performance, complementing what was discussed in part 2 regarding heat recovery and the efficient utilisation of thermal energy in industry.
Energy efficiency in industrial refrigeration does not depend solely on the quality of the installed equipment, but on the ability to orchestrate the entire system. This is where control and monitoring systems take centre stage.
Key Functions and Strategic Benefits of Control in Industrial Refrigeration
There are several core functions that enable effective control in industrial refrigeration — such as real-time monitoring and smart demand management. Learn more about these key features below.
Smart Demand Management
-
Time scheduling adapted to the actual usage of the installation.
-
Load prioritisation based on process criticality.
Energy Optimisation
-
Regulation of compressors, fans, and pumps according to actual load (variable speed control).
-
Seasonal efficiency algorithms: floating condensation, minimum superheat control, defrost optimisation.
Integration with Renewables and Energy Storage
-
Coupling with photovoltaic production to maximise self-consumption.
-
Use of thermal storage (water/glycol tanks) to shift cooling production to off-peak hours and cover demand peaks.
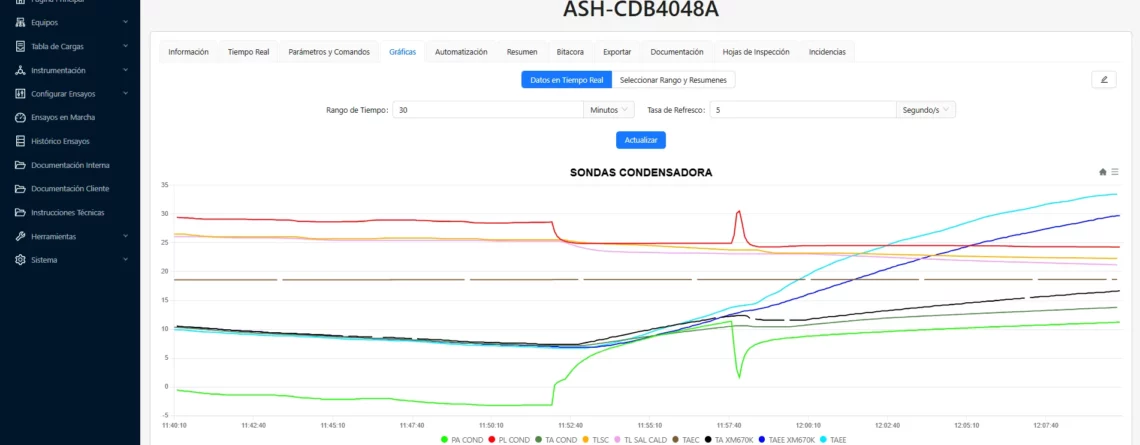
Real-Time Monitoring
-
Continuous supervision of energy performance (kWh per tonne of product, overall COP, etc.).
-
Early fault detection through alarms, preventing product loss and downtime.
-
Data traceability to justify energy savings and qualify for incentives such as Energy Savings Certificates (ESCs).
Strategic Benefits
An effective control system in industrial refrigeration provides significant strategic advantages, optimising both energy efficiency and plant performance:
-
Sustained energy savings: installations equipped with advanced control can reduce annual electricity consumption by 15–25%.
-
Higher reliability and longer equipment lifespan thanks to operation under optimal conditions.
-
Data-driven visibility and decision-making, aligning operational strategies with the company’s sustainability goals.
Application Examples
-
Defrost scheduling: concentrating defrost cycles during hours with surplus photovoltaic generation, avoiding electrical consumption during low renewable output periods.
-
Temperature setpoint management: adjusting room or equipment temperature setpoints during lower-cost tariff hours, directly reducing electricity bills.
-
Energy cost allocation: assigning and tracking energy costs by batch or product through detailed consumption monitoring.
This enables companies to determine the unit energy cost of production, identify less efficient processes, and improve overall profitability.